Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is the easiest and most common method for managing a Windows server. Included in all versions of Windows server and has a built-in client on all Windows desktops. There are also free applications available for Macintosh and Linux based desktops. Although, Windows 10 Home is equipped with Remote Desktop Client Software, it lacks the propriety RDP server from Microsoft, required for accessing remote computers. Enable Remote Desktop Using Settings. The easiest way to Enable Remote Desktop connection in Windows 10 is by going to Settings on your computer. Go to Settings System.
- Although, Windows 10 Home is equipped with Remote Desktop Client Software, it lacks the propriety RDP server from Microsoft, required for accessing remote computers. Enable Remote Desktop Using Settings. The easiest way to Enable Remote Desktop connection in Windows 10 is by going to Settings on your computer. Go to Settings System.
- Remote Desktop stuck at 'Securing remote connection'. Securing-remote-connection Question 5 7/3/2012 8:03:35 AM 9/2/2012 10:20:10 AM Preview Timeframe Windows.
How To Allow Remote Desktop Connection
This article provides a solution to the issue in which the remote desktop connection stays in the connecting to status.
Original product version: Windows 7 Service Pack 1, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: 2915774
Symptoms
Assume a scenario in which you use a remote desktop connection for operating system Windows 7 or later versions. In this scenario, Remote desktop connection is stuck for several seconds when it displays the following texts:
Remote Desktop Connection
Connecting to:
Securing remote connection...

Cause
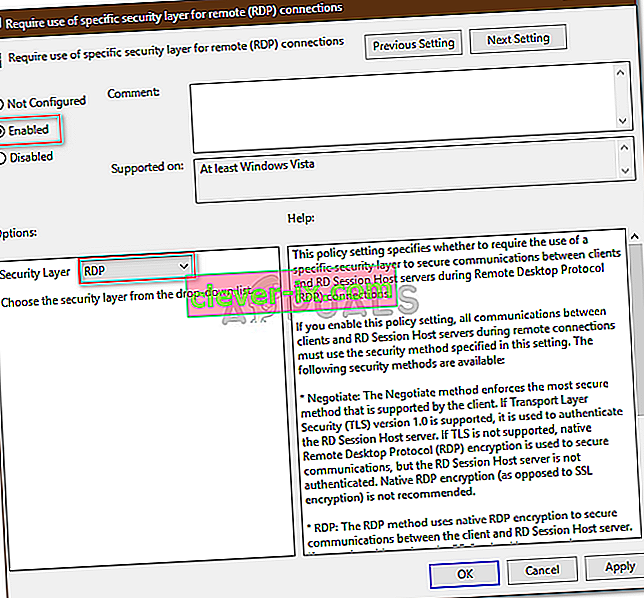
Remote desktop connection uses the highest possible security level encryption method between the source and destination.

In Windows 7 or later versions, the remote desktop connection uses the SSL (TLS 1.0) Protocol and the encryption is Certificate-based.
It means the authentication is performed by using self-signed certificates (default), or a certificate issued by a certification authority installed on the remote session host server (Terminal Server).
Windows 10 Rdp Securing Remote Connection Download
If you use a self-signed certificate, the system tries to retrieve the trusted certification authority list from the Internet to check the publish and revocation status of the certificate. Therefore, the Securing remote connection screen may appear for a while.
Workaround
To work around this behavior, use either of the following methods:
Method 1
If you're using a self-signed certificate, import the certificate to the source. To do this, follow these steps on the destination:
- Sign in as an administrator in the destination, select Start, enter mmc in the Search programs and files box and run Microsoft Management Console.
- On the File menu, select the Add/Remove Snap-in option.
- From the list of Available snap-ins, select Certificates and then select the Add button.
- On the Certificate Snap-in screen, select the Computer account check box and then select Next.
- On the Select Computer screen, select Local Computer and then select the Finish button.
- Go back to the Add/Remove Snap-In dialog box and then select the OK button.
- In the left pane of the console window, expand Console Route > Certificates (Local Computer) > Remote Desktop > Certificates.
- Double-click the Certificate in the middle pane to open it.
- On the Detail tab, select the Copy to File... button.
- The Certificate Export Wizard will open. Leave the default settings and then save the file in any folder.
- Copy the exported file to the source computer.
Then follow these steps on the source:
Sign in as an administrator in the source, select Start, enter mmc in the Search programs and files box, and run the mmc.exe.
Select the File menu and then select the Add/Remove Snap-in option.
From the list of Available snap-ins, select Certificates and then select the Add button.
On the Certificate Snap-in screen, select the Computer account check box and then select Next.
On the Select Computer screen, select Local Computer and then select the Finish button.
Go back to the Add/Remove Snap-In dialog box and then select the OK button.
In the left pane of the console window, expand Certificates (Local Computer) > Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates. Right-click to select All Tasks, and then select Import... from the menu.
The Certificate Import Wizard will open. Follow the instructions in the wizard to start the import.
In the Certificate file to import window, specify the file that was copied from the destination computer.
In the Certificate store window, verify that:
- Place all certificates in the following store is selected
- Certificate Store lists Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
Note
By default, the self-signed certificate expires in six months. If it has expired, the certificate will be recreated. You must import the recreated certificate to the source again.
Method 2
Deploy a Group Policy Object to the client to turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update. To do it, follow these steps on a Windows Server 2012 R2-based computer:
- Open Group Policy Management Console. To do it, hold the Windows key and press the r key. Type Gpmc.msc in the Run box, and then select OK.
- Create a new Group Policy Object (GPO) or select an existing Group Policy Object (GPO) to change.
- Right-click the selected Group Policy Object (GPO) and then select Edit and browse to the following Group Policy:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Internet Communication Management > Internet Communication settings - In the details pane, double-click Turn off Automatic Root Certificates Update, and then select Enabled.
